- シンクタンクならニッセイ基礎研究所 >
- 経済 >
- 経済予測・経済見通し >
- Japan's Economic Outlook for Fiscal Years 2023 to 2025 (November 2023)
Japan's Economic Outlook for Fiscal Years 2023 to 2025 (November 2023)

経済研究部 経済調査部長 斎藤 太郎
このレポートの関連カテゴリ
文字サイズ
- 小
- 中
- 大
2.Projection of Real GDP Growth
The July–September quarter of FY 2023 exhibited sluggishness in domestic and foreign demand, leading to negative growth (−2.1% on an annualized basis from the previous quarter) for the first time in three quarters. In the latter half of FY 2023, services exports are expected to rise, driven primarily by inbound-tourist demand; goods exports might remain sluggish due to the global economic slowdown. However, it is not anticipated that exports will be the primary engine of economic growth in the foreseeable future.
Meanwhile, private non-residential investment is expected to maintain its upward trajectory, supported by robust fixed investment by businesses. Additionally, a recovery in private consumption, especially in face-to-face services, is expected with the improvement in the employment and income environment, consistent with the normalization of socioeconomic activities. The growth of the Japanese economy is forecast to remain centered on domestic demand.
Real GDP is predicted to return to positive growth, reaching 1.7% in the October–December quarter of 2023 (on an annualized basis from the previous quarter). However, this growth is anticipated to slow, hovering around the zero range at 0.7% in the January–March quarter of 2024, primarily due to weakened exports.
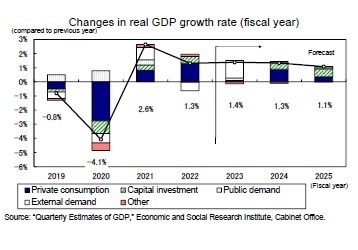 The scheduled tax cut included in the ongoing economic stimulus package is set to be implemented in June 2024, propelling a high rate of growth in private consumption of 2.8% on an annualized basis from the previous quarter in the July–September quarter of 2024. The effect of this tax cut is, however, expected to be temporary, with growth maintaining a steady pace of around 1% on an annualized basis from the October–December quarter of 2024 onwards.
The scheduled tax cut included in the ongoing economic stimulus package is set to be implemented in June 2024, propelling a high rate of growth in private consumption of 2.8% on an annualized basis from the previous quarter in the July–September quarter of 2024. The effect of this tax cut is, however, expected to be temporary, with growth maintaining a steady pace of around 1% on an annualized basis from the October–December quarter of 2024 onwards.Projections indicate that real GDP growth will persist at 1.4% in FY 2023, 1.3% in FY 2024, and 1.1% in FY 2025.
Inbound tourist demand, previously diminished due to the COVID-19 pandemic, has experienced rapid recovery following the phased relaxation and eventual elimination of border measures by April 2023. In October 2023, inbound visitors to Japan reached 2,516,500, surpassing 2019 levels for the same month and demonstrating a rebound in demand.
The share of visitors from China remains low, at 35.1% in October 2023 compared to the same month in 2019 and constituting about 30% of the total before the pandemic. However, an expected improvement in Japan–China relations could accelerate the overall growth in foreign visitors to Japan.
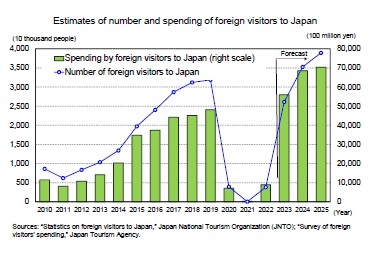 More notably, spending by foreign visitors surged: In the July–September quarter of 2023, their spending totaled 1.39 trillion yen, marking a 17.7% increase from the same period in 2019 and significantly surpassing pre-pandemic levels. This surge is attributed to factors such as a weaker yen and increased stays by business and other visitors.
More notably, spending by foreign visitors surged: In the July–September quarter of 2023, their spending totaled 1.39 trillion yen, marking a 17.7% increase from the same period in 2019 and significantly surpassing pre-pandemic levels. This surge is attributed to factors such as a weaker yen and increased stays by business and other visitors.The number of foreign visitors to Japan is expected to surpass 2019 levels by 2024 and exceed 31.88 million. Due to an increase in per capita spending attributed to the weak yen, inbound foreign travel consumption is expected to exceed the government target of 5 trillion yen by 2023 and expand to 7 trillion yen by 2025.
The core CPI rose to 4.2% in January 2023, the highest level in 41 years, but settled in the low 3% range from February onwards due to government measures to alleviate the pressure of electricity and city gas bills. In September, the CPI dipped to 2.8% year-on-year while the core CPI, excluding energy and fresh food, maintained a high level in the upper 4% range for six consecutive months, indicating persistent upward price pressure.
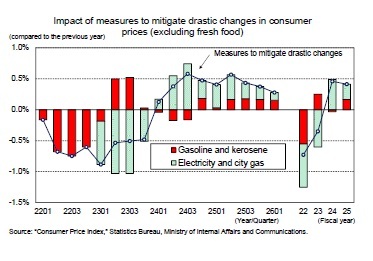 Measures to mitigate the effect of increases in fuel oil prices were extended due to yen depreciation and renewed increases in crude oil prices. These measures are expected to impact the core CPI, depressing its rate of increase until the October–December quarter of 2023 but boosting it from the January–March quarter of 2024 onwards.
Measures to mitigate the effect of increases in fuel oil prices were extended due to yen depreciation and renewed increases in crude oil prices. These measures are expected to impact the core CPI, depressing its rate of increase until the October–December quarter of 2023 but boosting it from the January–March quarter of 2024 onwards.
Please note: The data contained in this report has been obtained and processed from various sources, and its accuracy or safety cannot be guaranteed. The purpose of this publication is to provide information, and the opinions and forecasts contained herein do not solicit the conclusion or termination of any contract.
(2023年11月22日「Weekly エコノミスト・レター」)
このレポートの関連カテゴリ

03-3512-1836
- ・ 1992年:日本生命保険相互会社
・ 1996年:ニッセイ基礎研究所へ
・ 2019年8月より現職
・ 2010年 拓殖大学非常勤講師(日本経済論)
・ 2012年~ 神奈川大学非常勤講師(日本経済論)
・ 2018年~ 統計委員会専門委員
斎藤 太郎のレポート
| 日付 | タイトル | 執筆者 | 媒体 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025/10/03 | 雇用関連統計25年8月-失業率、有効求人倍率ともに悪化 | 斎藤 太郎 | 経済・金融フラッシュ |
| 2025/09/30 | 鉱工業生産25年8月-7-9月期は自動車中心に減産の可能性 | 斎藤 太郎 | 経済・金融フラッシュ |
| 2025/09/19 | 消費者物価(全国25年8月)-コアCPIは9ヵ月ぶりの3%割れ、年末には2%程度まで鈍化する見通し | 斎藤 太郎 | 経済・金融フラッシュ |
| 2025/09/17 | 貿易統計25年8月-関税引き上げの影響が顕在化し、米国向け自動車輸出が数量ベースで大きく落ち込む | 斎藤 太郎 | 経済・金融フラッシュ |
新着記事
-
2025年10月21日
選択と責任──消費社会の二重構造(2)-欲望について考える(3) -
2025年10月21日
連立協議から選挙のあり方を思う-選挙と同時に大規模な公的世論調査の実施を -
2025年10月21日
インバウンド消費の動向(2025年7-9月期)-量から質へ、消費構造の転換期 -
2025年10月21日
中国、社会保険料徴収をとりまく課題【アジア・新興国】中国保険市場の最新動向(71) -
2025年10月21日
今週のレポート・コラムまとめ【10/14-10/20発行分】
レポート紹介
-
研究領域
-
経済
-
金融・為替
-
資産運用・資産形成
-
年金
-
社会保障制度
-
保険
-
不動産
-
経営・ビジネス
-
暮らし
-
ジェロントロジー(高齢社会総合研究)
-
医療・介護・健康・ヘルスケア
-
政策提言
-
-
注目テーマ・キーワード
-
統計・指標・重要イベント
-
媒体
- アクセスランキング
お知らせ
-
2025年07月01日
News Release
-
2025年06月06日
News Release
-
2025年04月02日
News Release
【Japan's Economic Outlook for Fiscal Years 2023 to 2025 (November 2023)】【シンクタンク】ニッセイ基礎研究所は、保険・年金・社会保障、経済・金融・不動産、暮らし・高齢社会、経営・ビジネスなどの各専門領域の研究員を抱え、様々な情報提供を行っています。
Japan's Economic Outlook for Fiscal Years 2023 to 2025 (November 2023)のレポート Topへ


















 各種レポート配信をメールでお知らせ。読み逃しを防ぎます!
各種レポート配信をメールでお知らせ。読み逃しを防ぎます!




